What is deep sleep?
Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, is a state of sleep that occurs during the later stages of the sleep cycle. It is characterised by slow brain waves (delta waves) and is vital for physical and mental restoration.
During deep sleep, your breathing and heart rate slow down, and your muscles relax. This allows your body to repair any damage that has been done and restore energy levels. Naturally, we're not talking about significant damages but regular, daily wear and tear.

So, in its essence, deep sleep is the most essential segment of our sleep cycle. It's vital for a person's overall health and well-being, and it has been linked with numerous health benefits, but more on that later.
What happens with our bodies in the deep sleep stage?
First of all, our bodies slow down – tremendously. All our bodily functions, from brain activity and heart rate to metabolism and hormone production.
During the deep sleep stage, our bodies work hard to restore and rejuvenate us. This is when the majority of cell regeneration and tissue growth occurs. But – to achieve a deep sleep phase, we need to follow the healthy guidelines of sleep hygiene.
Our brains are also hard at work during this stage, as they are clearing out any toxins that have built up throughout the day. This detoxification process is essential for our cognitive health and helps to protect us against neurodegenerative diseases.

Deep sleep is also when we consolidate our memories from the day and store them for long-term memory. So, if you're trying to learn something new, make sure you get plenty of deep sleep!
As you can see, deep sleep is essential for our physical and mental health. Now let's take a look at:
What are the benefits of deep sleep?
It is possible to have a good night's sleep without getting deep sleep. Once we get older, we don't even need to worry about how much deep sleep we get. But, it goes without saying that more deep sleep is beneficial.
However, what are the benefits of it? Sleep experts say that they're many.
Energy & cell restoration
Deep sleep is essential for physical restoration. During this stage, our bodies heal and repair any damage that has been done. This includes things like cell regeneration and tissue growth (we'll get to that later).
Deep sleep is also when our energy levels are restored. If you're feeling tired during the day, it's because you didn't get enough deep sleep the night before. It doesn't matter if you went all day without tiring yourself physically – you can still benefit from entering the slow-wave sleep cycle.

But then again, this is why deep sleep is so important for athletes. They need to be well-rested in order to perform at their best and recover after a long day of hard training.
Increased blood flow
One of the benefits of deep sleep is increased blood flow. When we're in a state of deep sleep, our blood pressure drops and our blood vessels dilate (widen). This allows for more blood to flow to our muscles and tissues, which helps them to repair and grow.
This increased blood flow also helps to flush out any toxins or waste products that have built up in our bodies. This is an important process for maintaining our overall health and preventing chronic diseases.
Improved brain function
Deep sleep is essential for cognitive function and memory formation. As we mentioned before, deep sleep is when our brains clear out any toxins that have built up throughout the day. This process is essential for preventing neurodegenerative diseases and sleep disorders.

Boosting bones & tissues repair
Deep sleep is also when our bodies repair and grow bones and tissues. This process is essential for maintaining our overall health and preventing injuries.
There are a few reasons why deep sleep is so beneficial for bone and tissue repair.
First of all, deep sleep is when our bodies produce the most human growth hormone and other growth hormones. These hormones are essential for cell regeneration and tissue growth.
Secondly, deep sleep is when our blood pressure drops and our blood vessels dilate. This allows for more blood to flow to our muscles and tissues, which helps them to repair and grow.
Finally, during deep sleep, our brains clear out any toxins which could inhibit bone and tissue regeneration and growth.
What are the stages of sleep?
Understanding sleep stages and brain basics are essential to understanding deep sleep.
The brain is quite active during sleep, and different areas of the brain are more active at different times.
There are two categories (REM and non-REM) and four main stages of sleep: light sleep, deep sleep, REM sleep, and awake time.
But, more precisely, there are three non-REM stages and one REM stage of sleep through which we cycle during the night. Deep sleep occurs during the final stage of the non-REM stage.
Non-REM
As we fall asleep, our body enters the non-REM or NREM sleep stage. This stage is divided into three separate stages.
The first stage
The first stage of non-REM sleep is very light sleep from which we can easily be awakened. This stage only lasts for a few minutes as we transition from being awake to asleep.
During this stage:
- Our brain waves slow down
- Our eye movements, heartbeat and breathing slow down
- Our muscles relax with occasional twitches.

The second stage
During the second stage, our brain waves continue to slow, and our eye movements stop. This stage accounts for approximately 50 per cent of our sleep cycle, and we may spend more time in this stage than any other stage throughout the night.
During this stage:
- Our eye movements completely stop
- Our body temperature drops
- Our brain waves slow down to a halt, with occasional bursts of activity.

The third stage
The third and fourth stage is when we experience deep sleep. This is also referred to as “slow-wave sleep” (SWS) or delta sleep.
During these stages:
- Our heartbeat and breathing become very slow as our muscles relax
- Our brain waves become the slowest they will be during sleep
- It is difficult to be awakened by the noise.
The first stage of deep sleep lasts for anywhere from 45 to 90 minutes. It tends to last for longer periods in the first half of the night and becomes shorter with each sleep cycle.

REM sleep
After we move through the non-REM (non-rapid eye movement) stages, we enter REM (rapid eye movement) sleep.
Also called Stage 5, our first stage of REM sleep occurs about 90 minutes after we fall asleep. This is when we experience dreaming as our brain activity increases to a more wakeful state. We cycle through all four stages of sleep several times throughout the night, with the longest period of deep sleep occurring in the early morning hours.

During this stage:
- Our eyes move rapidly from side to side (hence the name)
- We experience dreaming as our brain activity increases, and we become more awake
- Our heart rate increases to near its waking state
- Our breathing becomes faster and even irregular at times
- Our limbs may even become paralyzed.
Why is deep sleep important?
We've outlined most of this stuff so far, but it's crucial that we sum it all up in one spot.
Deep sleep is important for both physical and mental health. It helps to restore and repair the body, and it also allows the brain to consolidate memories and process information.

Deep sleep is important for growth hormone secretion. Growth hormone is responsible for stimulating growth and development in children and adolescents, and it also helps to maintain muscle mass and bone density in adults. Deep sleep is the most important time for growth hormone secretion, so getting enough deep sleep is essential for good health.
Can lack of deep sleep lead to diseases?
There is a lot of research that suggests that a lack of deep sleep can lead to a variety of diseases.
Deep sleep is important for the brain to process information and memories from the day. If you don't get enough deep sleep, the brain can't convert information to memory properly, which can lead to conditions like Alzheimer's disease.
On the other hand, the lack of other restorative perks of deep sleep can lead to heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.

The deep sleep stage is also associated with disorders like sleepwalking, night terrors, bedwetting, and sleep eating. So if you're not getting enough deep sleep, it's important to talk to a doctor to see if there are any underlying health conditions that may be causing it.
How to deep-sleep more?
You don't need sleep medicine to help you get a good night's sleep. In fact, simply following a set of everyday rules can help you improve your sleep quality and achieve the deepest sleep of your life.
Daily exercise
The amount of deep sleep you get during the night is tied to how active you are during the day. A light workout session lasting no more than half an hour could help you achieve the best sleep of your life in a matter of days.

Follow a healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet is essential to getting healthy sleep. Avoiding foods that are high in sugar and simple carbohydrates can help you get more deep sleep at night. Also, be sure to eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, as these are great sources of vitamins and minerals that can help improve your sleep quality.

No coffee in the afternoon
Avoiding coffee in the afternoon can also help you sleep better at night. Caffeine can stay in your system for up to eight hours, so if you drink coffee late in the day, it could affect how much sleep you'll get that night.

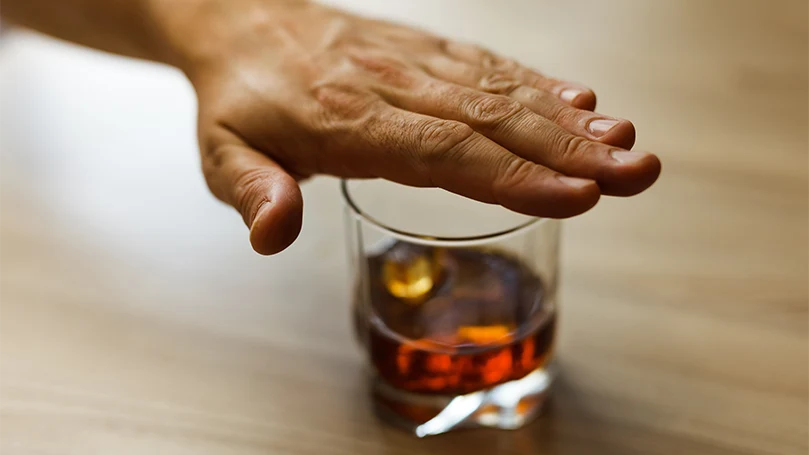
No alcohol
A nightcap isn't good if you want to get enough sleep. Alcohol can disrupt your sleep and prevent you from getting into the deepest stages of sleep. So, if you want to get enough deep sleep, it's best to avoid alcohol altogether or keep your daily intake to a minimum and at least four hours before bedtime.

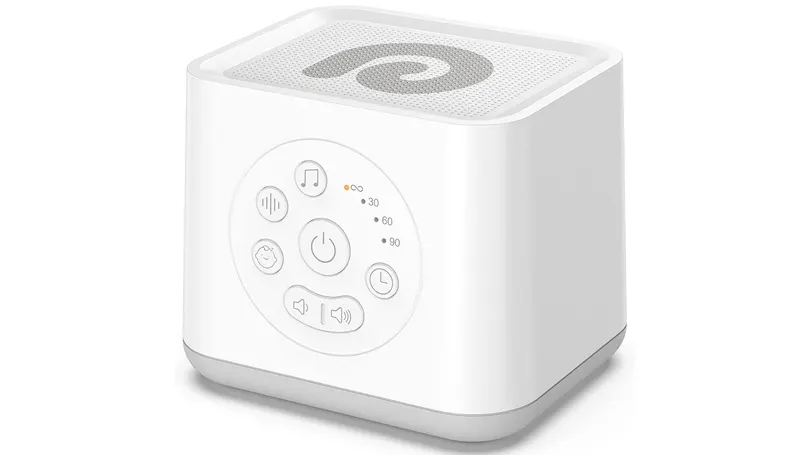
Listen to white noise if you have trouble falling asleep
White noise, pink noise, hypnosis tapes or even some low BPM music can help you fall asleep by relaxing and blocking external noise that might otherwise keep you awake. In fact, if you're looking for a way to get some deep sleep, turning on the white noise machine is a great first step. And even if it doesn't help you fall asleep right away, it will mask those outside noises that might keep you awake.
















There are no comments yet
"*" indicates required fields