Social jetlag explained

The internal body clock, known as your circadian rhythm, governs essential functions like sleep, hormone release, and even body temperature. Ideally, it's synchronised with the natural day-night cycle, encouraging you to sleep at night and stay awake during the day. This alignment is crucial for maintaining a regular sleep-wake cycle.
But what happens when this clock falls out of sync with your daily life, leading to an irregular sleep pattern?
That's where social jetlag comes into play!
Social jetlag is a term used to describe the misalignment between your body's internal clock and your daily activities and work schedule. It's like experiencing a time zone change without leaving your home. This phenomenon results in a difference in your sleep timing between workdays and your days off, disrupting the natural flow of your sleep-wake cycle.
Social jetlag is more widespread than you might think, affecting a significant portion of the population, with more than 80% of workers experiencing some degree of this circadian rhythm sleep disorder.
So, if you've ever struggled to wake up on weekdays while enjoying long, restful weekends, you're not alone in facing the challenges of an irregular sleep pattern and the consequences of a disrupted circadian rhythm.
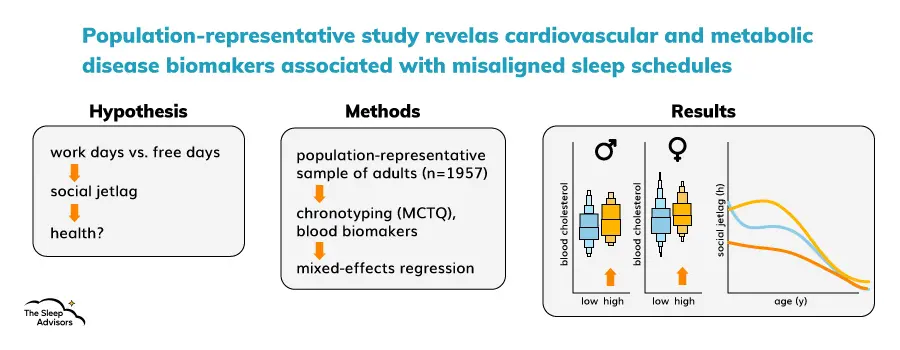
The study's mission
The study had three primary objectives:
- Understanding the link: Researchers aimed to investigate how social jetlag, in conjunction with our natural sleep preferences (known as chronotypes), affects various health markers.
- Identifying contributors: They sought to explore the factors contributing to social jetlag in our lives, shedding light on the causes behind this common issue.
- Work-from-home impact: The study also examined whether working from home could potentially reduce social jetlag, considering the recent surge in remote work.
The discoveries
The study meticulously analysed nine biomarkers related to metabolism, cardiovascular health, endocrine function, and the immune system.
- Cholesterol conundrum: Participants who reported higher levels of social jetlag exhibited elevated levels of total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. This association was particularly pronounced in those aged 50 and above, suggesting that social jetlag may be a hidden contributor to cardiovascular issues, especially as we age. The implications of this discovery could be significant for public health, potentially leading to new strategies for managing heart health.
- Chronotype matters: The study revealed that your natural sleep preference, whether you're an early bird or a night owl, plays a pivotal role in your overall health. Individuals with extreme morning and evening chronotypes were found to be at higher risk for cardiovascular disease risk factors, regardless of their level of social jetlag. This finding underscores the importance of considering our innate sleep tendencies when crafting sleep schedules and routines.
- Social jetlag contributors: Daily commuting, especially long commutes, emerged as a notable contributor. The stress and time pressures associated with managing busy work and social lives also played a role in disrupting sleep patterns.
- Working from home benefits: In a surprising twist, the research demonstrated that working from home positively impacted reducing social jetlag. The flexibility afforded by remote work allowed participants to align their work schedules more closely with their natural sleep preferences, resulting in improved sleep quality. This finding could have implications for the future of work, as more individuals and companies embrace remote work arrangements.
What does it mean for you?
While this study offers intriguing insights into the relationship between sleep, social jetlag, and health, it's important to note that it primarily identifies associations, not direct causal relationships. Further research is necessary to fully understand the complex interplay between these factors.
However, the implications for individuals are clear: paying attention to your sleep patterns and finding ways to align them better with your daily life could have profound implications for your long-term health and overall quality of life. Recognising the importance of your chronotype and adjusting to your daily routine accordingly could be a valuable step toward improved well-being.
Understanding chronotypes and health

Chronotypes are our genetically determined preferences for different times of the day. They are often classified into three categories: morning chronotypes (morning people), evening chronotypes (night owls), and intermediate chronotypes (neither strongly morning nor evening-oriented).
- Morning chronotypes tend to feel most alert and energetic in the early hours of the day and may naturally wake up early.
- Evening chronotypes, on the other hand, come alive in the evening and may find it challenging to wake up early in the morning.
- Intermediate chronotypes fall somewhere in between.
Research suggests that chronotype can influence various aspects of health. For example, morning chronotypes may have an advantage in terms of metabolic health, as their internal body clocks align more closely with the traditional nine-to-five workday. Evening chronotypes, however, may experience more social jetlag and face health challenges associated with misalignment between their internal clocks and societal schedules.
The possibility for future research
While this study provides crucial insights, it opens the door to many more questions. Researchers are eager to explore topics such as the impact of social jetlag and irregular sleep-wake syndrome on mental health, the potential long-term effects of remote work on sleep patterns, and personalised approaches to sleep management based on individual chronotypes. The journey to understanding the intricate relationship between sleep, health, and irregular sleep-wake syndrome is far from over.
Conclusion
Your sleep schedule isn't just about getting a good night's rest (or about improving the quality of your sleep); it's about safeguarding your overall health. As scientists continue to explore the mysteries of our internal biological clocks, stay tuned for further research on this captivating topic. In the meantime, we advise you to read the original sleep study that this article is based upon!
By understanding and actively managing social jetlag and aligning your sleep patterns with your chronotype, you can take proactive steps toward better health and well-being.














There are no comments yet
"*" indicates required fields